Overview of the base class structure¶
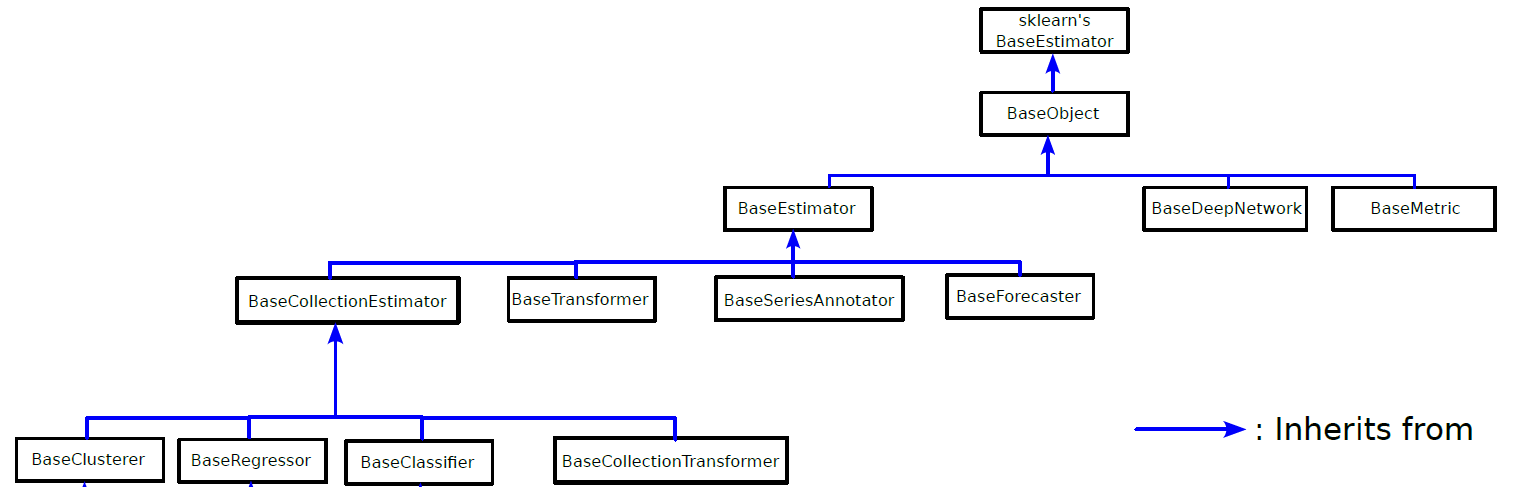
aeon uses a core inheritance hierarchy of classes across the toolkit, with specialised sub classes in each module. The basic class hierarchy is summarised in the following simplified UML
sklearn BaseEstimator and aeon BaseObject¶
To make sense of this, we break it down from the top.
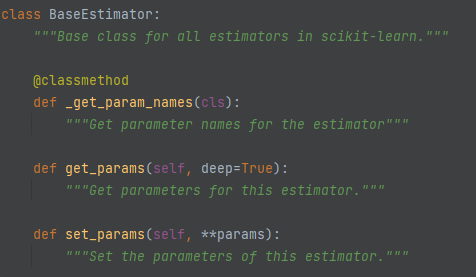
Everything inherits from sklearns BaseEstimator. This handles the mechanisms for getting and setting parameters. The code structure below is stylised to show the main functionality and may differ in details from the actual implementations.
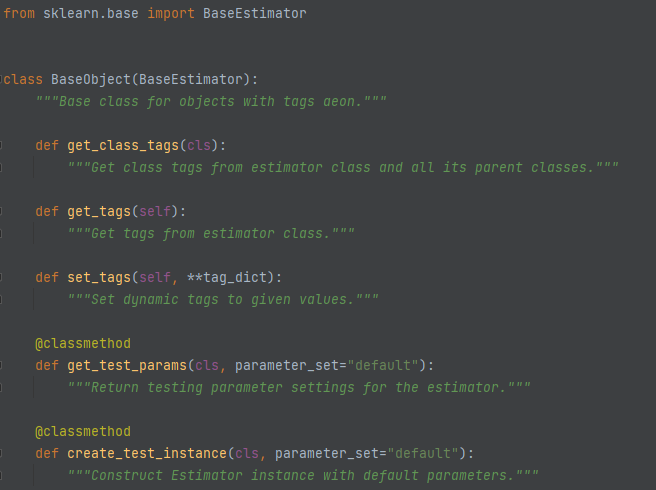
The aeon class BaseObject extends BaseEstimator and adds the tagging method and some other functionality used in aeon estimators
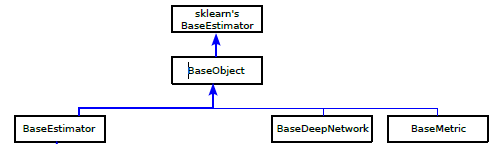
aeons BaseEstimator, BaseDeepNetwork and BaseMetric¶
Three classes extend BaseObject: BaseEstimator, BaseDeepNetwork and BaseMetric.
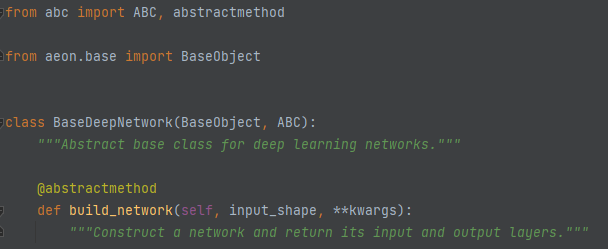
BaseDeepNetwork is the base class for all the deep learning networks defined in the networks module. It has a single abstract method build_network.
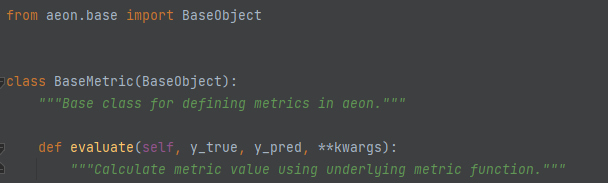
The BaseMetric class is the base class for forecasting performance metrics. It has a single abstract method evaluate.
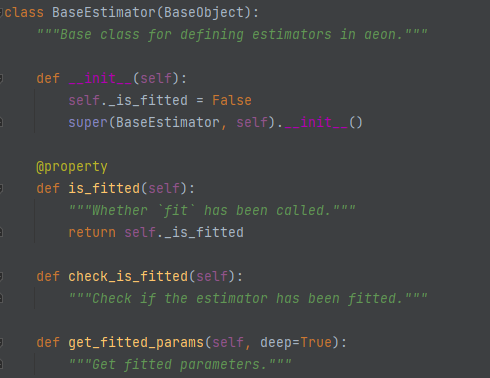
The BaseEstimator class is the base class for the majority of classes in aeon. Anything that uses fit and predict in aeon. It contains a protected attribute _is_fitted and checks as to the value of this attribute. It also has a method to get fitted parameters.
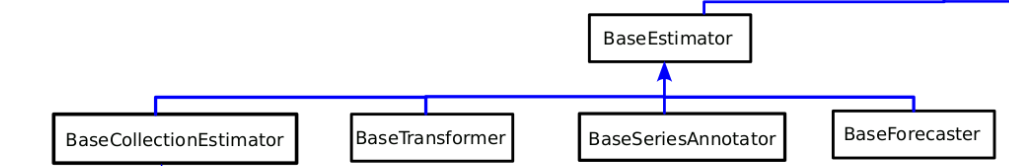
BaseEstimator has four direct base classes: BaseForecaster, BaseSeriesAnnotator, BaseTransformer and BaseCollectionEstimator.
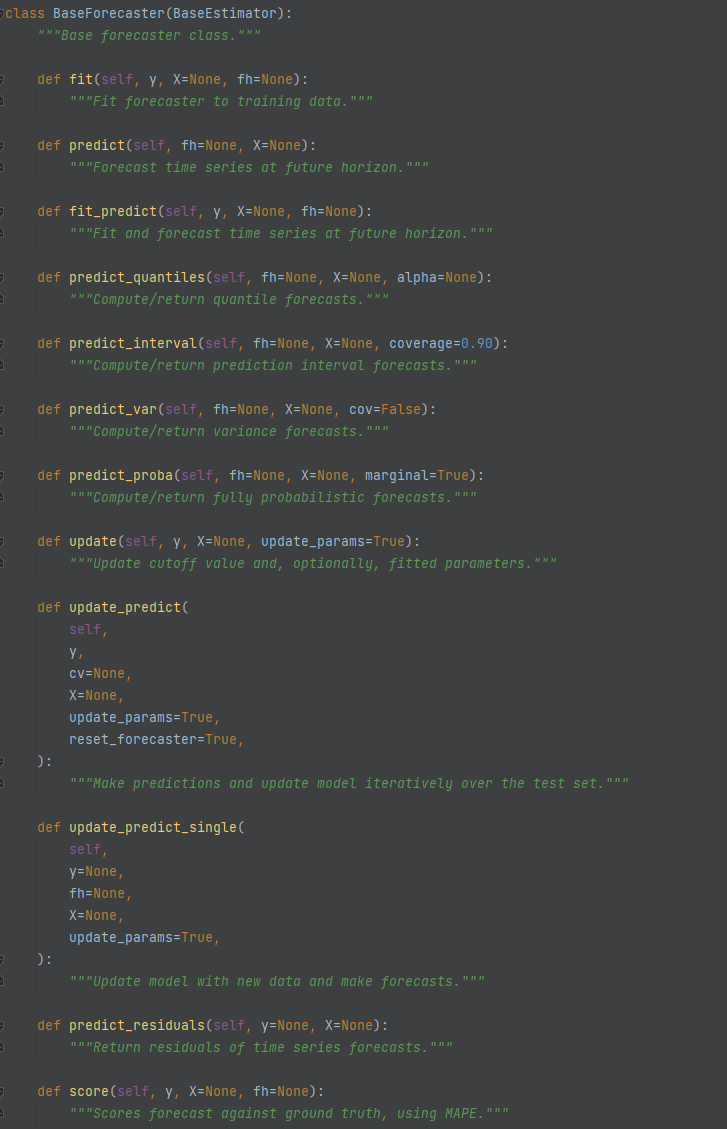
BaseForecaster (aeon.forecasting.base)¶
contains the forecasting specific methods. More details are available in the API. BaseForecaster has the following concrete methods:
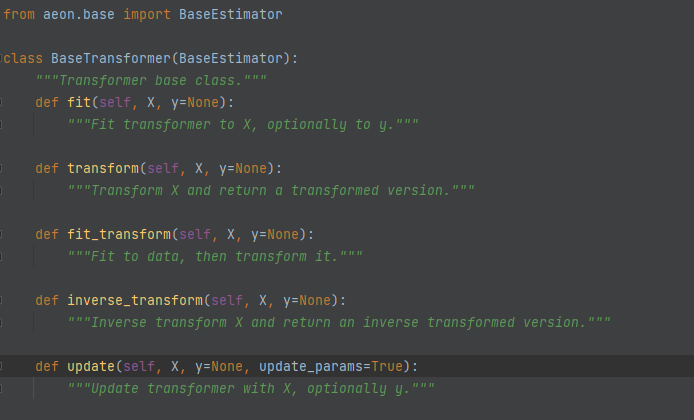
BaseTransformer (aeon.transformations.base)¶
Is the base class for all transformers, including single series transformers and collections transformers.
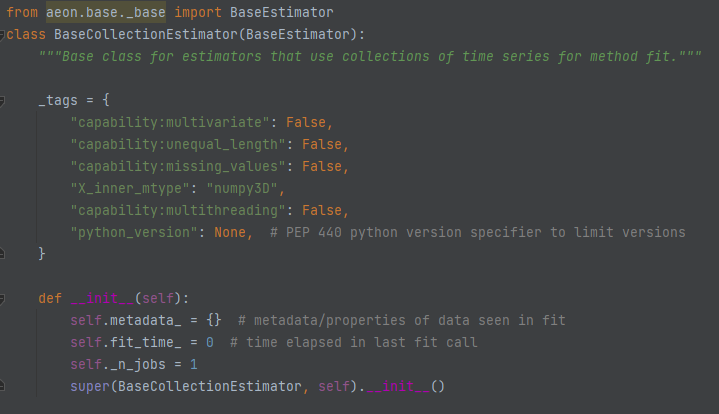
BaseCollectionEstimator (aeon.base)¶
Is the base class for estimators that construct models on collections of time series. This includes classifiers, clusterers, regressors and collection transformers. It contains attributes and tags common to all these estimators, and protected methods to perform checks and preprocessing common to all these estimators.
- transformer
- width:
700
- class:
no-scaled-link
The subclasses of BaseCollectionEstimator are as follows
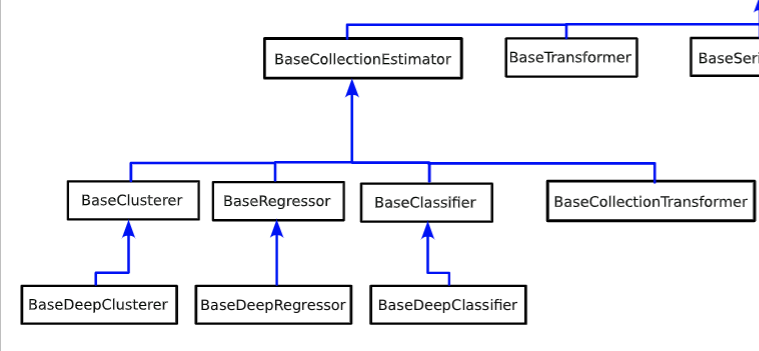
they have similar interfaces, but they are not identical
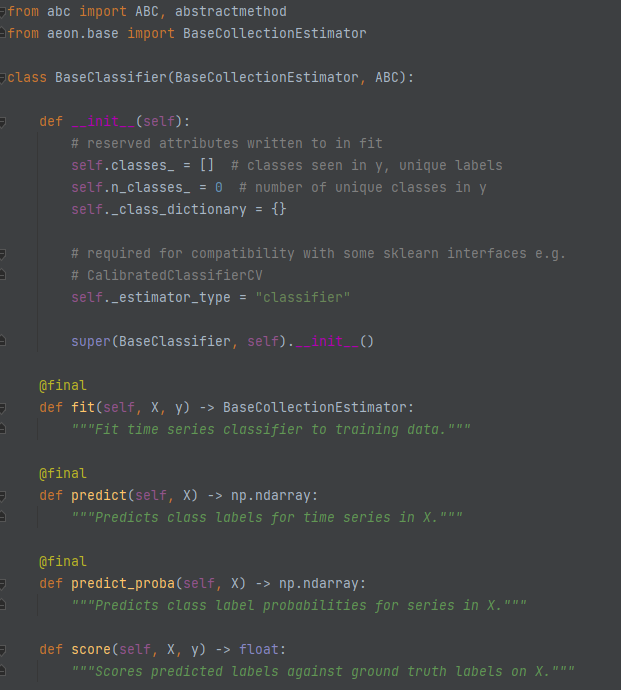
BaseClassifier (aeon.classification)¶
This is the base class for all classifiers. It uses the standard fit, predict and predict_proba structure from sklearn. fit and predict call the abstract methods _fit and _predict which are implemented in the subclass to define the classification algorithm. All of the common format checking and conversion is done using the following final methods defined in BaseCollectionEstimator.
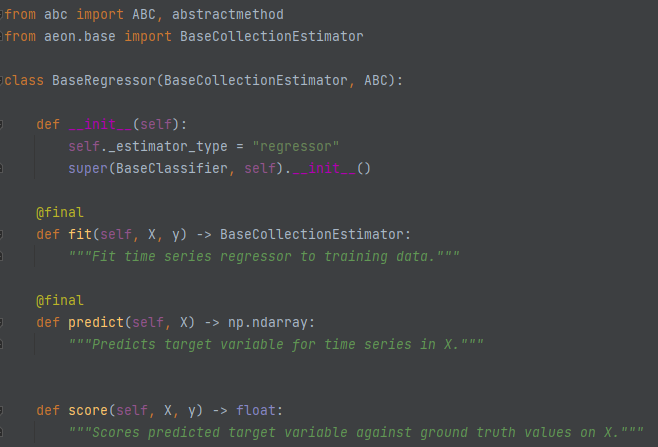
BaseRegressor (aeon.regression)¶
BaseRegressor has the same structure as BaseClassifier, although it has no predict_proba method. The tests on y are also different.
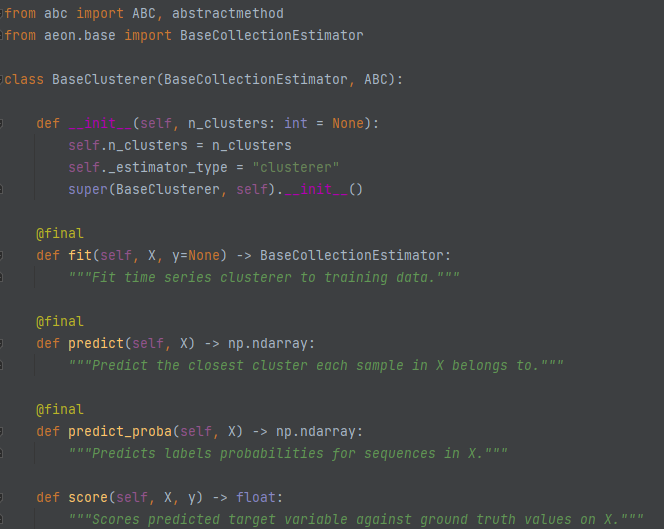
BaseClusterer (aeon.clustering)¶
BaseClusterer also has fit and predict, but does not take input y. It does include predict_proba.
- transformer
- width:
700
- class:
no-scaled-link
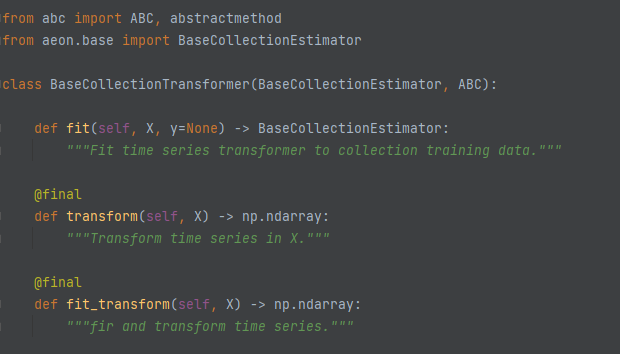
BaseCollectionTransformer (aeon.transformations.collection)¶
The BaseCollectionTransformer was introduced to differentiate transformers that work on a single series to those that work on collections. Part of the motivation was to work around a lot of legacy code in BaseTransformer that performs a huge amount of conversion checks that is unnecessary for collections. Rather than fit and predict it implements fit, transform and fit_transform.
- transformer
- width:
700
- class:
no-scaled-link
Generated using nbsphinx. The Jupyter notebook can be found here.