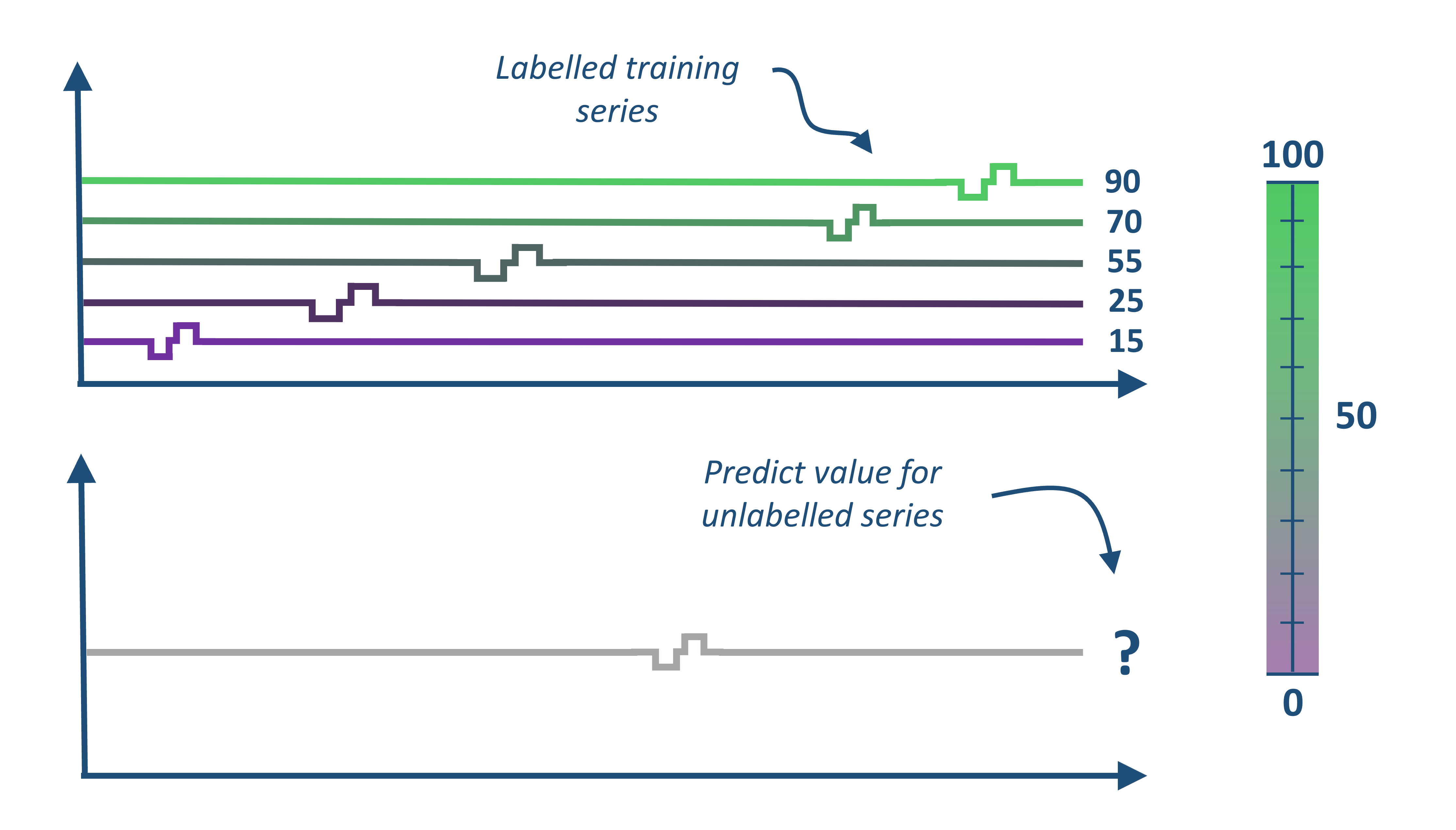
Time Series Regression (TSR) with aeon#
Time Series Classification (TSR) involves training a model from a collection of time series (real valued, ordered, data) in order to predict a continuous target variable.
There are two types of TSR.
Time Series Forecasting Regression (TSFR) relates to forecasting reduced to regression through a sliding window. This is the more familiar type to most people
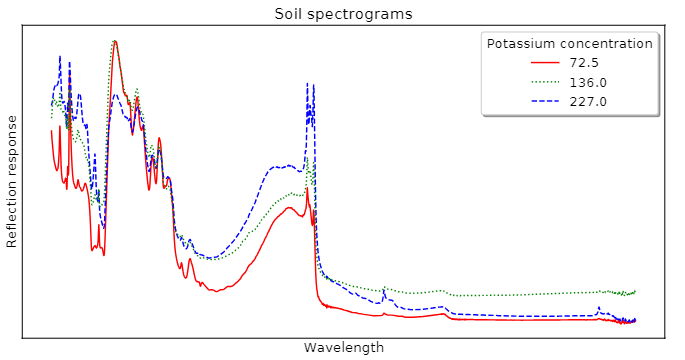
Time Series Extrinsic Regression (TSER). Tan et al. [1] formally specified a related, but distinct, type of time series regression problem: . Rather than being derived from a forecasting problem, TSER involves a predictive model built on time series to predict a real-valued variable distinct from the training input series. For example, shows soil spectrograms which can be used to estimate the potassium concentration. Ground truth is found through expensive lab based experiments that take some time. Spectrograms (ordered data series we treat as time series) are cheap to obtain and the data can be collected in any environment. An accurate regressor from spectrogram to concentration would make land and crop management more efficient.
Both types require time series regressors. aeon contain a range of regressors, broadly aligned with classifiers.
Data Storage and Problem Types#
Regressors and take time series input as either 3D numpy of shape (n_cases, n_channels, n_timepoints) for equal length series or as as a list of 2D numpy of length [n_cases]. All regressors work with equal length problems. Regression functionality for unequal length is currently limited.
aeon ships two example regression problems in the datasets module:
[1]:
import warnings
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from aeon.datasets import load_cardano_sentiment, load_covid_3month
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
covid_train, covid_trainy = load_covid_3month(split="train")
covid_test, covid_testy = load_covid_3month(split="test")
cardano_train, cardano_trainy = load_cardano_sentiment(split="train")
cardano_test, cardano_testy = load_cardano_sentiment(split="test")
covid_train.shape
[1]:
(140, 1, 84)
Covid 3 is from the monash tser archive who in turn got the data from WHO’s COVID-19 database. The goal of this dataset is to predict COVID-19’s death rate on 1st April 2020 for each country using daily confirmed cases for the last three months. This dataset contains 201 time series (140 train, 61 test), where each time series is the daily confirmed cases for a country. The data is univariate, each series length 84. Please refer to
[2]:
plt.title("First three cases for Covid3Month")
plt.plot(covid_train[0][0])
plt.plot(covid_train[1][0])
plt.plot(covid_train[2][0])
[2]:
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x26f42cfa6d0>]
[3]:
cardano_train.shape
[3]:
(74, 2, 24)
By combining historical sentiment data for Cardano cryptocurrency, extracted from EODHistoricalData and made available on Kaggle, with historical price data for the same cryptocurrency, extracted from CryptoDataDownload, we created the CardanoSentiment dataset, with 107 instances. The predictors are hourly close price (in USD) and traded volume during a day, resulting in 2-dimensional time series of length 24. The response variable is the normalized sentiment score on the day spanned by the timepoints.
[4]:
plt.title("First three cases for CardanoSentiment")
plt.plot(cardano_train[0][0])
plt.plot(cardano_train[1][0])
plt.plot(cardano_train[2][0])
[4]:
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x26f3093de20>]
Time Series Regressors in aeon#
All regressors inherit from the BaseRegressor class. Like classification and clustering, regressors have methods fit and predict to train and use the model. The list of regressors available can be found with all_estimators.
[5]:
from aeon.registry import all_estimators
all_estimators("regressor", as_dataframe=True)
[5]:
| name | estimator | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | CNNRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.deep_learning.cnn.CNNR... |
| 1 | Catch22Regressor | <class 'aeon.regression.feature_based._catch22... |
| 2 | DummyRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression._dummy.DummyRegressor'> |
| 3 | FreshPRINCERegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.feature_based._fresh_p... |
| 4 | InceptionTimeRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.deep_learning.inceptio... |
| 5 | IndividualInceptionRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.deep_learning.inceptio... |
| 6 | KNeighborsTimeSeriesRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.distance_based._time_s... |
| 7 | RegressorPipeline | <class 'aeon.regression.compose._pipeline.Regr... |
| 8 | RocketRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.convolution_based._roc... |
| 9 | SklearnRegressorPipeline | <class 'aeon.regression.compose._pipeline.Skle... |
| 10 | TapNetRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.deep_learning.tapnet.T... |
| 11 | TimeSeriesForestRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.interval_based._tsf.Ti... |
Currently we have three deep learning, two feature based, one convolution based and one distance based regressors, in addition to utility regressors such as Dummy.
[6]:
from aeon.datasets import load_covid_3month
from aeon.regression.distance_based import KNeighborsTimeSeriesRegressor
covid_train, covid_trainy = load_covid_3month(split="train")
covid_test, covid_testy = load_covid_3month(split="test")
knn = KNeighborsTimeSeriesRegressor()
knn.fit(covid_train, covid_trainy)
p = knn.predict(covid_test)
sse = np.sum((covid_testy - p) * (covid_testy - p))
sse
[6]:
0.17823940618016532
Multivariate Classification#
Nearly all of the regressors can handle multivariate data
[7]:
all_estimators(
"regressor", filter_tags={"capability:multivariate": True}, as_dataframe=True
)
[7]:
| name | estimator | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | CNNRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.deep_learning.cnn.CNNR... |
| 1 | Catch22Regressor | <class 'aeon.regression.feature_based._catch22... |
| 2 | DummyRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression._dummy.DummyRegressor'> |
| 3 | FreshPRINCERegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.feature_based._fresh_p... |
| 4 | InceptionTimeRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.deep_learning.inceptio... |
| 5 | IndividualInceptionRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.deep_learning.inceptio... |
| 6 | KNeighborsTimeSeriesRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.distance_based._time_s... |
| 7 | RocketRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.convolution_based._roc... |
| 8 | TapNetRegressor | <class 'aeon.regression.deep_learning.tapnet.T... |
[8]:
from aeon.regression import DummyRegressor
fp = KNeighborsTimeSeriesRegressor()
dummy = DummyRegressor()
dummy.fit(cardano_train, cardano_trainy)
knn.fit(cardano_train, cardano_trainy)
pred = knn.predict(cardano_test)
res_knn = cardano_testy - pred
res_dummy = cardano_testy - dummy.predict(cardano_test)
plt.title("Raw residuals")
plt.plot(res_knn)
plt.plot(res_dummy)
[8]:
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x26f4ba77160>]
References [1] Tan et al. “Time series extrinsic regression”, Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 35(3), 2021 [2] Guijo-Rubio et al. “Unsupervised Feature Based Algorithms for Time Series Extrinsic Regression”, ArXiv, 2023
Generated using nbsphinx. The Jupyter notebook can be found here.